 High
HighStudy design
Design:
Study group formation:
Time period of study:
Primary outcome domains examined:
Increase short-term earnings, Increase long-term earnings, Increase very long-term earnings, Increase short-term employment, Increase long-term employment, Increase very long-term employment, Decrease very long-term benefit receipt, Increase education and trainingOther outcome domains examined:
Job characteristics, housing, assets and debts, and financial distressStudy funded by:
Results
Scroll to the right to view the rest of the table columns
| Outcome domain | Measure | Timing | Study quality by finding | Comparison group mean | Intervention group mean | Impact | Units | Findings | Sample size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Increase short-term earnings | Annual earnings | Year 1 |
High 
|
10,721.00 | 8,920.00 | -1,801.00 | 2007 dollars |

|
410 |
| Increase short-term earnings | Annual earnings | Year 1 |
High 
|
11,895.00 | 10,177.00 | -1,718.00 | 2007 dollars |

|
343 |
| Increase long-term earnings | Annual earnings | Year 5 |
High 
|
20,331.00 | 24,311.00 | 3,980.00 | 2011 dollars |
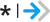
|
410 |
| Increase long-term earnings | Annual earnings | Year 5 |
High 
|
20,773.00 | 24,818.00 | 4,045.00 | 2011 dollars |
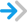
|
343 |
| Increase very long-term earnings | Annual earnings | Year 11 |
High 
|
30,884.00 | 35,500.00 | 4,616.00 | 2019 dollars |

|
410 |
| Increase very long-term earnings | Annual earnings | Year 6 |
High 
|
23,124.00 | 28,204.00 | 5,080.00 | 2012 dollars |
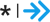
|
343 |
| Increase very long-term earnings | Annual earnings | Year 9 |
High 
|
28,404.00 | 33,644.00 | 5,240.00 | 2015 dollars |

|
410 |
| Increase short-term employment | Employed in every month, annual | Year 1 |
High 
|
57.10 | 72.00 | 14.90 | Percentage points |

|
343 |
| Increase short-term employment | Ever employed, quarterly | Quarter 6 |
High 
|
69.00 | 63.00 | -6.00 | Percentage points |

|
410 |
| Increase long-term employment | Employed in every month, annual | Year 5 |
High 
|
59.20 | 66.60 | 7.40 | Percentage points |

|
343 |
| Increase long-term employment | Ever employed, quarterly | Quarter 20 |
High 
|
71.00 | 81.00 | 10.00 | Percentage points |

|
410 |
| Increase very long-term employment | Employed in every month, annual | Year 6 |
High 
|
44.80 | 45.00 | 0.20 | Percentage points |

|
343 |
| Increase very long-term employment | Ever employed, annual | Year 11 |
High 
|
73.70 | 83.80 | 10.10 | Percentage points |

|
410 |
| Increase very long-term employment | Ever employed, quarterly | Quarter 36 |
High 
|
74.00 | 82.00 | 8.00 | Percentage points |

|
410 |
| Decrease very long-term benefit receipt | Currently receive Food Stamps/SNAP | Year 6 |
High 
|
28.40 | 21.70 | -6.70 | Percentage points |

|
343 |
| Decrease very long-term benefit receipt | Currently receive SSI | Year 6 |
High 
|
4.60 | 6.00 | 1.40 | Percentage points |

|
343 |
| Decrease very long-term benefit receipt | Currently receive WIC | Year 6 |
High 
|
13.80 | 9.60 | -4.20 | Percentage points |

|
343 |
| Decrease very long-term benefit receipt | Received unemployment benefits | Year 11 |
High 
|
5.70 | 7.30 | 1.60 | Percentage points |

|
410 |
| Increase education and training | Earned a bachelor's degree | Year 11 |
High 
|
5.66 | 4.04 | -1.62 | Percentage points |

|
410 |
| Increase education and training | Earned a certificate or degree from a training program | Year 11 |
High 
|
12.60 | 24.90 | 12.30 | Percentage points |

|
410 |
| Increase education and training | Earned a college degree | Year 6 |
High 
|
26.30 | 18.20 | -8.10 | Percentage points |

|
343 |
| Increase education and training | Earned a vocational certificate or license | Year 6 |
High 
|
49.10 | 72.60 | 23.50 | Percentage points |

|
343 |
| Increase education and training | Earned an associate's degree | Year 11 |
High 
|
14.90 | 16.30 | 1.40 | Percentage points |

|
410 |
 High
High Moderate
Moderate
The findings quality describe our confidence that a given study’s finding is because of the intervention. We do not display findings that rate low.
 A moderate-to-large favorable finding that is unlikely to be due to chance
A moderate-to-large favorable finding that is unlikely to be due to chance A moderate-to-large favorable finding that might to be due to chance
A moderate-to-large favorable finding that might to be due to chance A small favorable finding that is unlikely to be due to chance
A small favorable finding that is unlikely to be due to chance A small favorable finding that might be due to chance
A small favorable finding that might be due to chance A favorable finding that is unlikely to be due to chance, but we cannot determine the standardized effect size
A favorable finding that is unlikely to be due to chance, but we cannot determine the standardized effect size A favorable finding that might be due to chance, but we cannot determine the standardized effect size
A favorable finding that might be due to chance, but we cannot determine the standardized effect size A moderate-to-large unfavorable finding that is unlikely to be due to chance
A moderate-to-large unfavorable finding that is unlikely to be due to chance A moderate-to-large unfavorable finding that might to be due to chance
A moderate-to-large unfavorable finding that might to be due to chance A small unfavorable finding that is unlikely to be due to chance
A small unfavorable finding that is unlikely to be due to chance A small unfavorable finding that might be due to chance
A small unfavorable finding that might be due to chance An unfavorable finding that is unlikely to be due to chance, but we cannot determine the standardized effect size
An unfavorable finding that is unlikely to be due to chance, but we cannot determine the standardized effect size An unfavorable finding that might be due to chance, but we cannot determine the standardized effect size
An unfavorable finding that might be due to chance, but we cannot determine the standardized effect size A finding that is unlikely to be due to chance, but we cannot determine the standardized effect size or direction
A finding that is unlikely to be due to chance, but we cannot determine the standardized effect size or direction A finding of no effect that might be due to chance
A finding of no effect that might be due to chance
Sample characteristics
The study included a sample of 410 participants pursuing health care–related jobs. Most study participants were female (88 percent) and were, on average, age 30. About three-quarters (74 percent) were Latino, 14 percent were African American, and 10 percent were White. All participants had at least a high school diploma or GED, with 70 percent having earned a high school diploma, 25 percent a GED, and 5 percent a college degree. In total, 84 percent of participants had been employed in the year before study enrollment, with average annual earnings of $11,722.
Age
| Mean age | 30 years |
Sex
| Female | 88% |
| Male | 12% |
Participant race and ethnicity
| Black or African American | 14% |
| White, not Hispanic | 10% |
| Unknown or not reported | 3% |
| Hispanic or Latino of any race | 74% |
The race and ethnicity categories may sum to more than 100 percent if the authors reported race and ethnicity separately; in these cases, we report the category White, rather than White, not Hispanic.
Family status
| Married | 28% |
Participant employment and public benefit status
| Had low incomes | 100% |
Participant education
| Had a high school diploma or GED | 100% |
Specific employment barriers
| Were experiencing homelessness | 1% |
Intervention implementation
Implementing organization:
Program history:
Intervention services:
Mandatory services:
Comparison services:
Service receipt duration:
Intervention funding:
Cost information:
These figures are based on cost information reported by study authors. The Pathways Clearinghouse converted that information to a single amount expressed in 2018 dollars; for details, see the FAQ. This information is not an official price tag or guarantee.
Study publications
Elliott, Mark, and Anne Roder (2017). Escalating gains: Project QUEST’s sectoral strategy pays off, New York: Economic Mobility Corporation. Available at https://economicmobilitycorp.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/Escalating-Gains_WEB.pdf.
Roder, Anne, and Mark Elliott (2018). Escalating gains: The elements of Project QUEST’s success, New York: Economic Mobility Corporation. Available at https://economicmobilitycorp.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Elements-of-Project-QUESTs-Success.pdf.
Roder, Anne, and Mark Elliott (2019). Nine year gains: Project QUEST's continuing impact, New York: Economic Mobility Corporation. Available at https://economicmobilitycorp.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/NineYearGains_web.pdf.
Roder, Anne, and Mark Elliott (2021). Eleven year gains: Project QUEST's investment continues to pay dividends, New York: Economic Mobility Corporation. Available at https://economicmobilitycorp.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/Mobility_Eleven-Year-Gains.pdf.
View the glossary for more information about these and other terms used on this page.
The Pathways Clearinghouse refers to interventions by the names used in study reports or manuscripts. Some intervention names may use language that is not consistent with our style guide, preferences, or the terminology we use to describe populations.

25209-Project Quality Empl