 High
HighStudy design
Design:
Study group formation:
Time period of study:
Primary outcome domains examined:
Increase short-term earnings, Increase long-term earnings, Increase short-term employment, Increase long-term employment, Decrease short-term benefit receipt, Decrease long-term benefit receiptOther outcome domains examined:
Housing, Child well-beingStudy funded by:
Results
Scroll to the right to view the rest of the table columns
| Outcome domain | Measure | Timing | Study quality by finding | Impact | Units | Findings | Sample size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Increase short-term earnings | Earnings over 6 months | months 13-18 |
High 
|
-76.00 | 2001 dollars |

|
8,664 |
| Increase long-term earnings | Earnings over 6 months | months 31-36 |
High 
|
72.00 | 2003 dollars |
|
8,664 |
| Increase short-term employment | Average quarterly employment rate | quarters 5-6 |
High 
|
-0.01 | percentage points |

|
8,664 |
| Increase short-term employment | Number of quarters employed | Quarter 5 |
High 
|
-0.07 | quarters |
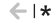
|
8,664 |
| Increase long-term employment | Average quarterly employment rate | quarters 11-12 |
High 
|
0.00 | percentage points |

|
8,664 |
| Increase long-term employment | Number of quarters employed | 3 years |
High 
|
-0.06 | quarters |

|
8,664 |
| Decrease short-term benefit receipt | Average quarterly receipt of Food Stamps | 1.5 years |
High 
|
0.03 | percentage points |

|
5,056 |
| Decrease short-term benefit receipt | Average quarterly receipt of TANF benefits | 1.5 years |
High 
|
0.02 | percentage points |

|
7,622 |
| Decrease short-term benefit receipt | Food Stamps benefits received over 6 months | months 13-18 |
High 
|
46.00 | 2001 dollars |

|
5,056 |
| Decrease short-term benefit receipt | TANF benefits received over 6 months | months 13-18 |
High 
|
29.00 | 2001 dollars |

|
7,622 |
| Decrease long-term benefit receipt | Average quarterly receipt of Food Stamps | 3.5 years |
High 
|
0.02 | percentage points |

|
5,056 |
| Decrease long-term benefit receipt | Average quarterly receipt of TANF benefits | 3.5 years |
High 
|
0.01 | percentage points |

|
7,622 |
| Decrease long-term benefit receipt | Food Stamp benefits received over 6 months | months 31-36 |
High 
|
34.00 | 2003 dollars |

|
5,056 |
| Decrease long-term benefit receipt | TANF benefits received over 6 months | months 31-36 |
High 
|
43.00 | 2003 dollars |

|
7,622 |
 High
High Moderate
Moderate
The findings quality describe our confidence that a given study’s finding is because of the intervention. We do not display findings that rate low.
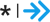 A moderate-to-large favorable finding that is unlikely to be due to chance
A moderate-to-large favorable finding that is unlikely to be due to chance A moderate-to-large favorable finding that might to be due to chance
A moderate-to-large favorable finding that might to be due to chance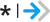 A small favorable finding that is unlikely to be due to chance
A small favorable finding that is unlikely to be due to chance A small favorable finding that might be due to chance
A small favorable finding that might be due to chance A favorable finding that is unlikely to be due to chance, but we cannot determine the standardized effect size
A favorable finding that is unlikely to be due to chance, but we cannot determine the standardized effect size A favorable finding that might be due to chance, but we cannot determine the standardized effect size
A favorable finding that might be due to chance, but we cannot determine the standardized effect size A moderate-to-large unfavorable finding that is unlikely to be due to chance
A moderate-to-large unfavorable finding that is unlikely to be due to chance A moderate-to-large unfavorable finding that might to be due to chance
A moderate-to-large unfavorable finding that might to be due to chance A small unfavorable finding that is unlikely to be due to chance
A small unfavorable finding that is unlikely to be due to chance A small unfavorable finding that might be due to chance
A small unfavorable finding that might be due to chance An unfavorable finding that is unlikely to be due to chance, but we cannot determine the standardized effect size
An unfavorable finding that is unlikely to be due to chance, but we cannot determine the standardized effect size An unfavorable finding that might be due to chance, but we cannot determine the standardized effect size
An unfavorable finding that might be due to chance, but we cannot determine the standardized effect size A finding that is unlikely to be due to chance, but we cannot determine the standardized effect size or direction
A finding that is unlikely to be due to chance, but we cannot determine the standardized effect size or direction A finding of no effect that might be due to chance
A finding of no effect that might be due to chance
Sample characteristics
To be eligible to receive a Welfare-to-Work voucher, families had to be former or current Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (TANF) recipients, or they needed to be eligible to receive TANF benefits. They also had to meet the standard Housing Choice Voucher eligibility requirements. Individual sites might have further specified the eligibility requirements. The individuals in the research sample were predominantly female, never married, and were between 19 and 44 years old. In addition, nearly half of the sample was Black and non-Hispanic, 21 percent was Hispanic, and 20 percent was White and non-Hispanic. Nearly 57 percent had a high school diploma or GED.
Age
| Mean age | 31 years |
Sex
| Female | 92% |
| Male | 8% |
Participant race and ethnicity
| Black or African American | 50% |
| White, not Hispanic | 20% |
| Another race | 8% |
| Unknown or not reported | 1% |
| Hispanic or Latino of any race | 21% |
The race and ethnicity categories may sum to more than 100 percent if the authors reported race and ethnicity separately; in these cases, we report the category White, rather than White, not Hispanic.
Family status
| Married | 17% |
Participant employment and public benefit status
| Were employed | 45% |
| Were unemployed | 54% |
| Were eligible for or receiving cash assistance | 100% |
| Had low incomes | 100% |
Participant education
| Did not have a high school diploma or GED | 35% |
Specific employment barriers
| Had limited work histories | 19% |
Intervention implementation
Implementing organization:
Program history:
Intervention services:
Mandatory services:
Comparison services:
Service receipt duration:
Intervention funding:
Study publications
Mills, Gregory, Daniel Gubits, Larry L. Orr, David Long, Judith Feins, Bulbul Kaul, Michelle Wood, Amy Jones and Associates, Cloudburst Consulting, and QED Group (2006). Effects of housing vouchers on welfare families: Final report, Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development. Available at https://www.huduser.gov/portal/publications/commdevl/hsgvouchers.html.
Patterson, Rhiannon, Michelle Wood, Ken Lam, Satyendra Patrabansh, Gregory Mills, Steven Sullivan, Hiwotte Amare, and Lily Zandniapour (2004). Evaluation of the Welfare to Work Voucher program: Report to Congress, Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development. Available at https://www.huduser.gov/portal/publications/pubasst/welfrwrk.html.
View the glossary for more information about these and other terms used on this page.
The Pathways Clearinghouse refers to interventions by the names used in study reports or manuscripts. Some intervention names may use language that is not consistent with our style guide, preferences, or the terminology we use to describe populations.

3170-Evaluation of the We